« User Manual 4.0 Angles and Intervals » : différence entre les versions
m Admin a déplacé la page Angles and Intervals vers User Manual 4.0 Angles and Intervals sans laisser de redirection |
Aucun résumé des modifications |
||
| (5 versions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
__NOTOC__ | |||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
=== Scope === | === Scope === | ||
| Ligne 7 : | Ligne 6 : | ||
=== Javadoc === | === Javadoc === | ||
The angle-related objects are available in the package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.math.interval</code> in the PATRIUS library. The class defining an interval end point, though, is in the package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils</code>. | The angle-related objects are available in the package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.math.interval</code> in the PATRIUS library. The class defining an interval end point, though, is in the package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils</code>. | ||
|=Library| | |||
|Patrius |[{{ | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|Patrius |[{{ | |- | ||
! scope="col"| Library | |||
! scope="col"| Javadoc | |||
|- | |||
|Patrius | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/math/interval/package-summary.html Package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.math.interval] | |||
|- | |||
|Patrius | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/utils/package-summary.html Package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils] | |||
|} | |||
=== Links === | === Links === | ||
| Ligne 18 : | Ligne 26 : | ||
=== Package Overview === | === Package Overview === | ||
The package < | The package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils</code> contains the class IntervalEndPoint that defines the type of boundary (CLOSED, OPEN) of an interval end. | ||
</ | |||
The package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils</code> contains the actual angle-related classes. | The package <code>fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils</code> contains the actual angle-related classes. | ||
| Ligne 29 : | Ligne 36 : | ||
An interval is made of two endpoints, and each endpoint may be closed or opened. | An interval is made of two endpoints, and each endpoint may be closed or opened. | ||
This is the most generic implementation of intervals : the class | This is the most generic implementation of intervals : the class <code>GenericInterval<T></code>. The enumeration provides the endpoint types : CLOSED and OPEN. | ||
This class is meant to be used as a parent class for all intervals implementations. | This class is meant to be used as a parent class for all intervals implementations. | ||
| Ligne 37 : | Ligne 44 : | ||
The class is immutable, in the sense that the endpoints objects are set at the interval creation. | The class is immutable, in the sense that the endpoints objects are set at the interval creation. | ||
'''Mutable types should not be used as endpoint value types!''' | |||
Examples : | Examples : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
final IntervalEndpointType lowType = IntervalEndpointType.OPEN; | |||
final Double lowValue = new Double(34.56); | |||
final IntervalEndpointType upType = IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED; | |||
final Double upValue = new Double(-2.3e34); | |||
// Note the order of values is off : this class cannot enforce an order | |||
final GenericInterval<Double> tgi = new GenericInterval<Double>(lowType, lowValue, upValue, upType); | |||
final Double gLow = tgi.getLowerData(); | |||
assertTrue(gLow.equals(lowValue)); | |||
assertTrue | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Please see the Javadoc for more information. | Please see the Javadoc for more information. | ||
| Ligne 62 : | Ligne 68 : | ||
=== Comparable intervals === | === Comparable intervals === | ||
This implementation of intervals, | This implementation of intervals, <syntaxhighlight lang="java">ComparableInterval<T extends Comparable<T>></syntaxhighlight>, is for types implementing the Comparable interface ( for instance : <code>Integer</code>, <code>Double</code>). | ||
This implementation inherits from | This implementation inherits from <code>GenericInterval<T></code>; in addition to inherited capabilities, it enforces a proper order on the lower and upper endpoints. A <code>ComparableInterval</code> can also tell : | ||
* if a given value is inside an interval | * if a given value is inside an interval | ||
| Ligne 82 : | Ligne 88 : | ||
Due to numerical quality issues, the algorithm is the following : | Due to numerical quality issues, the algorithm is the following : | ||
- If the interval is of the form [a, a + 2Pi[, then | - If the interval is of the form [a, a + 2Pi[, then | ||
if x < a and x + 2Pi >= a + 2Pi, the angle is set to a (numerical quality issue due to the non-iqual repartition of real values around lower and upper boundaries) | if x < a and x + 2Pi >= a + 2Pi, the angle is set to a (numerical quality issue due to the non-iqual repartition of real values around lower and upper boundaries) | ||
if x = 2Pi, the angle is set to a | if x = 2Pi, the angle is set to a | ||
- If the interval is of the form ]a, a + 2Pi], then | |||
- If the interval is of the form ]a, a + 2Pi], then | |||
if x > a + 2Pi and x – 2Pi <= a, the angle is set to a + 2Pi (numerical quality issue due to the non-iqual repartition of real values around lower and upper boundaries) | if x > a + 2Pi and x – 2Pi <= a, the angle is set to a + 2Pi (numerical quality issue due to the non-iqual repartition of real values around lower and upper boundaries) | ||
if x = a, the angle is set to a + 2Pi | if x = a, the angle is set to a + 2Pi | ||
- Else | |||
- Else | |||
if x < a, the angle is set to x + 2Pi | if x < a, the angle is set to x + 2Pi | ||
if x > a + 2Pi, the angle is set to x- 2Pi | if x > a + 2Pi, the angle is set to x- 2Pi | ||
| Ligne 104 : | Ligne 108 : | ||
Hereunder is given a code example illustrating how the <code>ComparableInterval</code> object behaves: | Hereunder is given a code example illustrating how the <code>ComparableInterval</code> object behaves: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
final Double d1 = new Double(-4.44); | |||
final Double d2 = new Double(2.22); | |||
final Double d3 = new Double(6.23); | |||
final Double d4 = new Double(8.72); | |||
final IntervalEndpointType open = IntervalEndpointType.OPEN; | |||
final IntervalEndpointType closed = IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED; | |||
// Interval : [ -4.44 ; 2.22 [ | |||
final ComparableInterval<Double> ti1 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(closed, d1, d2, open); | |||
final Double inside1 = new Double(-4.44); | |||
final Double inside2 = new Double(-2.24); | |||
final Double outside1 = new Double(-0.2313E96); | |||
final Double outside2 = new Double(-4.45); | |||
assertTrue(ti1.contains(inside1)); | |||
assertTrue | assertTrue(ti1.contains(inside2)); | ||
assertTrue | assertTrue(!ti1.contains(outside1)); | ||
assertTrue | assertTrue(!ti1.contains(outside2)); | ||
assertTrue | // Two open overlapping intervals | ||
// ] d1 ; d3 [ | |||
// ...] d2 ; d4 [ | |||
final ComparableInterval<Double> ovo1 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(open, d1, d3, open); | |||
final ComparableInterval<Double> ovo2 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(open, d2, d4, open); | |||
assertTrue(ovo1.overlaps(ovo2)); | |||
assertTrue | assertTrue(ovo2.overlaps(ovo1)); | ||
assertTrue | // Two closed intervals, first includes second | ||
// [ d1 .....;..... d4 ] | |||
// .....[ d2 ; d3 ] | |||
final ComparableInterval<Double> clos1 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(closed, d1, d4, closed); | |||
final ComparableInterval<Double> clos2 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(closed, d2, d3, closed); | |||
assertTrue(clos1.includes(clos2)); | |||
assertTrue | assertTrue(!clos2.includes(clos1)); | ||
assertTrue | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== Angle intervals === | === Angle intervals === | ||
| Ligne 257 : | Ligne 260 : | ||
=== Classes === | === Classes === | ||
Here is a summary of the most important classes : | Here is a summary of the most important classes : | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! scope="col"| Class | |||
! scope="col"| Summary | |||
! scope="col"| Javadoc | |||
|- | |||
|'''IntervalEndpointType''' | |||
|Defines an interval end point as OPEN or CLOSED. | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/math/interval/IntervalEndpointType.html ...] | |||
|- | |||
|'''AngleInterval''' | |||
|Implements an interval of angles, taking angles' modulus into account. | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/math/interval/AngleInterval.html ...] | |||
|- | |||
|'''AngleTools''' | |||
|Provides several angle-related utility methods. | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/math/interval/AngleTools.html ...] | |||
|- | |||
|'''GenericInterval''' | |||
|Implements a generic interval. | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/math/interval/GenericInterval.html ...] | |||
|- | |||
|'''AbsoluteDateInterval''' | |||
|This class implements an interval based on the AbsoluteDate class using the ComparableInterval class. | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/time/AbsoluteDateInterval.html ...] | |||
|- | |||
|'''ComparableInterval''' | |||
|The class describe an interval of Comparable data. | |||
|[{{JavaDoc4.0}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/math/interval/ComparableInterval.html ...] | |||
|} | |||
[[Category:User_Manual_4.0_Mathematics]] | |||
Dernière version du 2 mars 2018 à 15:33
Introduction
Scope
This section describes how angles, intervals and angle intervals are defined and used in the PATRIUS library.
Javadoc
The angle-related objects are available in the package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.math.interval in the PATRIUS library. The class defining an interval end point, though, is in the package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils.
| Library | Javadoc |
|---|---|
| Patrius | Package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.math.interval |
| Patrius | Package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils |
Links
None as of now.
Useful Documents
None as of now.
Package Overview
The package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils contains the class IntervalEndPoint that defines the type of boundary (CLOSED, OPEN) of an interval end.
The package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.utils contains the actual angle-related classes.
Features Description
Generic intervals
An interval is made of two endpoints, and each endpoint may be closed or opened.
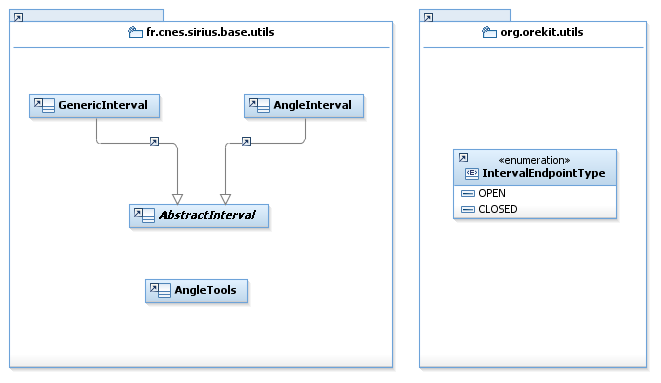
This is the most generic implementation of intervals : the class GenericInterval<T>. The enumeration provides the endpoint types : CLOSED and OPEN.
This class is meant to be used as a parent class for all intervals implementations.
This class makes no assumption on the nature of the parameter class T, so it may create intervals of anything- but the functionality for this class is limited (we only have getters for the endpoints values, and their type). That's why it's meant to be used as a parent class.
The class is immutable, in the sense that the endpoints objects are set at the interval creation.
Mutable types should not be used as endpoint value types!
Examples :
final IntervalEndpointType lowType = IntervalEndpointType.OPEN;
final Double lowValue = new Double(34.56);
final IntervalEndpointType upType = IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED;
final Double upValue = new Double(-2.3e34);
// Note the order of values is off : this class cannot enforce an order
final GenericInterval<Double> tgi = new GenericInterval<Double>(lowType, lowValue, upValue, upType);
final Double gLow = tgi.getLowerData();
assertTrue(gLow.equals(lowValue));
Please see the Javadoc for more information.
Example with doubles: interval [1.0, 2.0[ :
GenericInterval<Double> interval = new GenericInterval<Double>(IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED, 1.0, 2.0, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN);
Comparable intervals
This implementation of intervals,
ComparableInterval<T extends Comparable<T>>
, is for types implementing the Comparable interface ( for instance : Integer, Double).
This implementation inherits from GenericInterval<T>; in addition to inherited capabilities, it enforces a proper order on the lower and upper endpoints. A ComparableInterval can also tell :
- if a given value is inside an interval
- if an interval is inside another
- if two intervals overlap
Please see the Javadoc for more information.
Angle intervals
The AngleInterval class represents an interval of doubles that shall be used to deal with angles. It contains the end points values and types (enum OPENED and CLOSED, class IntervalEndPointType), the mid value (“reference”) and the interval length.
Angle tools
This class is a toolbox containing static methods to perform operations on angles, for instance :
- angleInInterval : sets an angle in an interval modulo 2Pi
Due to numerical quality issues, the algorithm is the following :
- If the interval is of the form [a, a + 2Pi[, then
if x < a and x + 2Pi >= a + 2Pi, the angle is set to a (numerical quality issue due to the non-iqual repartition of real values around lower and upper boundaries)
if x = 2Pi, the angle is set to a
- If the interval is of the form ]a, a + 2Pi], then
if x > a + 2Pi and x – 2Pi <= a, the angle is set to a + 2Pi (numerical quality issue due to the non-iqual repartition of real values around lower and upper boundaries)
if x = a, the angle is set to a + 2Pi
- Else
if x < a, the angle is set to x + 2Pi
if x > a + 2Pi, the angle is set to x- 2Pi
else the angle is x
- angle comparisons
- supplementary, complementary angles computation
Getting Started
Comparable intervals
Hereunder is given a code example illustrating how the ComparableInterval object behaves:
final Double d1 = new Double(-4.44);
final Double d2 = new Double(2.22);
final Double d3 = new Double(6.23);
final Double d4 = new Double(8.72);
final IntervalEndpointType open = IntervalEndpointType.OPEN;
final IntervalEndpointType closed = IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED;
// Interval : [ -4.44 ; 2.22 [
final ComparableInterval<Double> ti1 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(closed, d1, d2, open);
final Double inside1 = new Double(-4.44);
final Double inside2 = new Double(-2.24);
final Double outside1 = new Double(-0.2313E96);
final Double outside2 = new Double(-4.45);
assertTrue(ti1.contains(inside1));
assertTrue(ti1.contains(inside2));
assertTrue(!ti1.contains(outside1));
assertTrue(!ti1.contains(outside2));
// Two open overlapping intervals
// ] d1 ; d3 [
// ...] d2 ; d4 [
final ComparableInterval<Double> ovo1 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(open, d1, d3, open);
final ComparableInterval<Double> ovo2 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(open, d2, d4, open);
assertTrue(ovo1.overlaps(ovo2));
assertTrue(ovo2.overlaps(ovo1));
// Two closed intervals, first includes second
// [ d1 .....;..... d4 ]
// .....[ d2 ; d3 ]
final ComparableInterval<Double> clos1 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(closed, d1, d4, closed);
final ComparableInterval<Double> clos2 = new ComparableInterval<Double>(closed, d2, d3, closed);
assertTrue(clos1.includes(clos2));
assertTrue(!clos2.includes(clos1));
Angle intervals
Two constructors are available for an AngleInterval instance :
- One needing directly the end points values and types. Its signature is in the writing order. For example, to create [0.0, 2PI[ :
AngleInterval angleInterval1 = new AngleInterval(IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED, 0.0,
MathUtils.TWO_PI, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN);
- One needing the reference and length values, and the end points nature. Here, the signature is : “reference”, “length”, “lower end point type”, “upper end point type”. To create [-PI, PI[ :
AngleInterval angleInterval1 = new AngleInterval(0.0, MathUtils.TWO_PI,
IntervalEndpointType.CLOSED, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN);
Those constructors throw an exception « MathIllegalArgumentException » if the interval is not valid. It is considered not valid if :
- The length is strictly greater than 2PI
- The length is equal to 2PI and both end points are “closed”
- The length is negative
- The length is zero and at least one end point is opened (an interval with only one double in it is accepted)
Those intervals are impossible to modify once created : they have no setters. To get an interval with different values, a new one shall be constructed.
Angle tools
The method "angleInInterval"
The method « angleInInterval » computes the (2PI) modulus of an angle (given as a double) in an angle interval (AngleInterval object) :
- If a (2PI) modulus of the input angle exists in the interval, its value is returned. Because the angles have a maximum length of 2PI with at least an open end point, there can be only one solution.
- If no value in the interval is a solution, it means the operation is impossible with the given inputs, and a « MathIllegalArgumentException » is thrown.
Use example :
try {
// Angle
double angle = 6*FastMath.PI;
// Interval creation
AngleInterval angleInterval = new AngleInterval(IntervalEndpointType.OPEN,
- MathUtils.HALF_PI, MathUtils.HALF_PI, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN);
// angle in interval
double result = AngleTools.angleInInterval(angle, angleInterval);
}
catch (MathIllegalArgumentException e) {
// correct catch!
}
« result » value is here 0.0 : the modulus of 6PI in ]-PI/2,-PI/2[
Comparisons methods
The comparison methods available in the AngleTools class are the same as the one for doubles in the « Comparators » class : relative comparisons using a default epsilon. Input angles are only expressed in the input interval before the comparison.
If the computation in the interval of one of the input angles is not possible, a « MathIllegalArgumentException » is thrown.
Use example :
try {
// Angle
double angle1 = 6*FastMath.PI;
double angle2 = 4*FastMath.PI + 0.1;
// Interval creation
AngleInterval angleInterval = new AngleInterval(IntervalEndpointType.OPEN,
- MathUtils.HALF_PI, MathUtils.HALF_PI, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN);
// angle in interval
boolean isLowerOrEqual = AngleTools.lowerOrEqual(angle1, angle2, angleInterval);
}
catch (MathIllegalArgumentException e) {
// correct catch !
}
Both angles are here computable in the given interval. The first one is lower than the second once in the interval : the returned result is “true”
Supplementary, complementary and opposite angles
The tools box AngleTools proposes the methods to compute supplementary (method supplementaryAngle), complementary (method complementaryAngle) and opposite (method oppositeAngle) angles, taking into account an angle interval (of the type AngleInterval previously described)
Those methods first compute a common supplementary, complementary or opposite angle, and then try to express the result in the given interval. If this last operation is not possible, an exception is thrown (MathIllegalArgumentException).
Use example :
try {
// Interval creation
AngleInterval angleInterval = new AngleInterval(IntervalEndpointType.OPEN,
- MathUtils.HALF_PI, MathUtils.HALF_PI, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN);
// computation
double angle = 3.0/4.0*FastMath.PI + 6.0*FastMath.PI;
double res = AngleTools.supplementaryAngle(angle, angleInterval);
}
catch (MathIllegalArgumentException e) {
// correct catch !
}
The result is here computable, its value is PI/4.
Contents
Interfaces
None as of now.
Classes
Here is a summary of the most important classes :
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| IntervalEndpointType | Defines an interval end point as OPEN or CLOSED. | ... |
| AngleInterval | Implements an interval of angles, taking angles' modulus into account. | ... |
| AngleTools | Provides several angle-related utility methods. | ... |
| GenericInterval | Implements a generic interval. | ... |
| AbsoluteDateInterval | This class implements an interval based on the AbsoluteDate class using the ComparableInterval class. | ... |
| ComparableInterval | The class describe an interval of Comparable data. | ... |