« User Manual 3.3 Elliptic cylinder » : différence entre les versions
Aller à la navigation
Aller à la recherche
Page créée avec « ====Definition==== The elliptic cylinders are defined in a 3D space by their origin, their local frame, their height and the two radii defining the elliptic basis : Fil... » |
Aucun résumé des modifications |
||
| Ligne 5 : | Ligne 5 : | ||
====Implementation==== | ====Implementation==== | ||
The Elliptic Cylinder object in the SIRIUS library implements the [ | The Elliptic Cylinder object in the SIRIUS library implements the [[User Manual 3.3 The Cylinder Interface|cylinder interface]]. Please refer to the [{{JavaDoc3.3}}/org/apache/commons/math3/geometry/euclidean/threed/EllipticCylinder.html Javadoc] for a complete list of public methods. | ||
====Instantiation==== | ====Instantiation==== | ||
Dernière version du 4 avril 2018 à 14:22
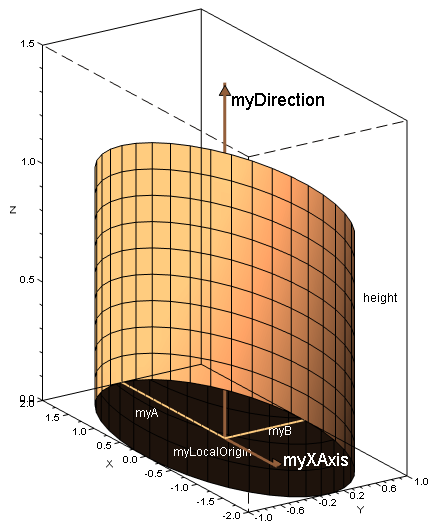
Definition
The elliptic cylinders are defined in a 3D space by their origin, their local frame, their height and the two radii defining the elliptic basis :
Implementation
The Elliptic Cylinder object in the SIRIUS library implements the cylinder interface. Please refer to the Javadoc for a complete list of public methods.
Instantiation
The object is built from three vectors (Vector3D) and three doubles :
Vector3D originCone = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
Vector3D direction = new Vector3D(2.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Vector3D inputUvector = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
double radiusA = 4.0;
double radiusB = 2.0;
double height = 5.0;
EllipticCylinder cylinder = new EllipticCylinder(originCone, direction, inputUvector, radiusA, radiusB, height);
The local frame is built such as :
- W is the direction vector once normalized
- U is orthogonal to W and its direction is defined by the 'input U vector"
- V completes the frame
Usage
Please refer to the [MAT_GEO_Home#HInteractions Interactions with other geometrical objects section] for methods inherited from the Shape interface.