« User Manual 3.3 Environment Models » : différence entre les versions
| Ligne 194 : | Ligne 194 : | ||
The PATRIUS <code>org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides</code> package provides tools allowing the user to use Terestrial and Ocean tides. The <code>org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides.coefficients</code> package also allows reading external ocean tides coefficients data files. The following file formats are supported by PATRIUS: | The PATRIUS <code>org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides</code> package provides tools allowing the user to use Terestrial and Ocean tides. The <code>org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides.coefficients</code> package also allows reading external ocean tides coefficients data files. The following file formats are supported by PATRIUS: | ||
* FES2004 format | * FES2004 format | ||
==== Reference point displacement ==== | ==== Reference point displacement ==== | ||
The PATRIUS <code>org.orekit.utils.ReferencePointsDisplacement</code> class provides a model describing the displacement of reference points due to the effect of the solid Earth tides. The computation is performed by the static method'''solidEarthTidesCorrections(AbsoluteDate, Vector3D, Vector3D, Vector3D)'''. The implemented model has been validated by comparison with tests available in the IERS website. The example below shows the user how to compute displacements of reference points: | The PATRIUS <code>org.orekit.utils.ReferencePointsDisplacement</code> class provides a model describing the displacement of reference points due to the effect of the solid Earth tides. The computation is performed by the static method '''solidEarthTidesCorrections(AbsoluteDate, Vector3D, Vector3D, Vector3D)'''. The implemented model has been validated by comparison with tests available in the IERS website. The example below shows the user how to compute displacements of reference points: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
// Test from source ftp://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/chapter7/dehanttideinel/DEHANTTIDEINEL.F | |||
// date : 13/04/2009 | // date : 13/04/2009 | ||
| Ligne 221 : | Ligne 219 : | ||
Assert.assertEquals(0.05516568152597246810, disp.getZ(), Precision.EPSILON); | Assert.assertEquals(0.05516568152597246810, disp.getZ(), Precision.EPSILON); | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== Geomagnetic models === | === Geomagnetic models === | ||
Version du 28 février 2018 à 10:00
Introduction
Scope
The scope of this section is to present the physical models available through the Orekit library.
Javadoc
All the classes related to physical models are in the org.orekit.forces and org.orekit.parameterpackages. The classes related to reading potential files are in the package org.orekit.forces.gravity.potential of the Orekit library.
| Library | Javadoc |
|---|---|
| Orekit addons | Package org.orekit.forces.atmospheres |
| Orekit addons | Package org.orekit.forces.atmospheres.solarActivity |
| Orekit | Package org.orekit.forces.atmospheres.solarActivity.specialized |
| Orekit addons | Package org.orekit.forces.atmospheres.solarActivity.specialized |
| Orekit | Package org.orekit.forces.gravity.potential |
| Orekit addons | Package org.orekit.forces.gravity.variations |
| Orekit addons | Package org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides.coefficients |
| Orekit | Package org.orekit.parameter |
| Orekit addons | Class org.orekit.utils.ReferencePointsDisplacement |
Links
Some useful links are given hereunder.
IERS Page IERS Conventions (2010), Technical Note No.36
Project Pages
- NASA - Crustal Dynamics Data Information System (CDDIS)
- GFZ - Grace (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment) Mission Homepage
- GFZ - International Centre for Global Earth Models
- Groupe de Recherche de Géodésie Spatiale
Results Pages
- EGM96: The NASA GSFC and NIMA Joint Geopotential Model, Lemoine; F. G., Kenyon; S. C., Factor; J. K., Trimmer; R.G., Pavlis; N. K., Chinn; D. S., Cox; C. M., Klosko; S. M., Luthcke; S. B., Torrence; M. H., Wang; Y. M., Williamson; R. G., Pavlis; E. C., Rapp; R. H., Olson; T. R., NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland, 20771 USA, July 1998, Available here.
- GFZ : Global Gravity Field Models, Available here.
Useful Documents
Package Overview
Features Description
Earth Potential Models
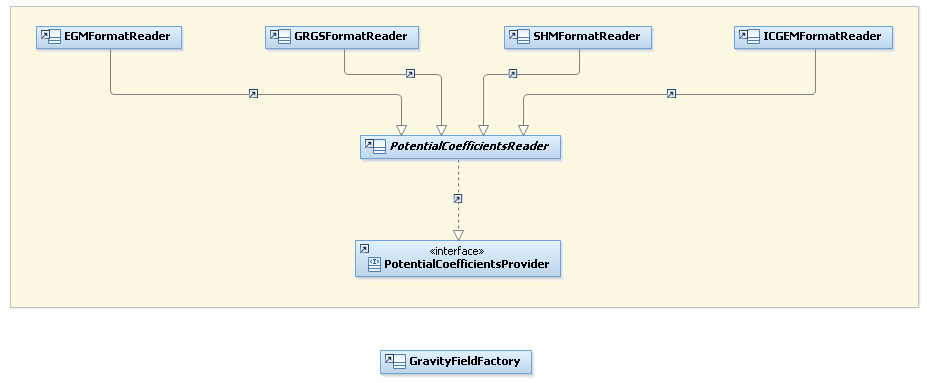
The Orekit org.orekit.forces.gravity.potential package provides tools allowing the user to read external gravity potential data files. The following file formats are supported by Orekit :
- EGM96 ASCII format data
- EIGEN-GRACE format
- ICGEM format
- GRGS format
Below is a diagram showing the architecture of the org.orekit.forces.gravity.potential package.
For a detailed explanation of the Orekit Data Management System, please refer to the [SUP_DMS_Home Data Management System section] of the Support User Manual.
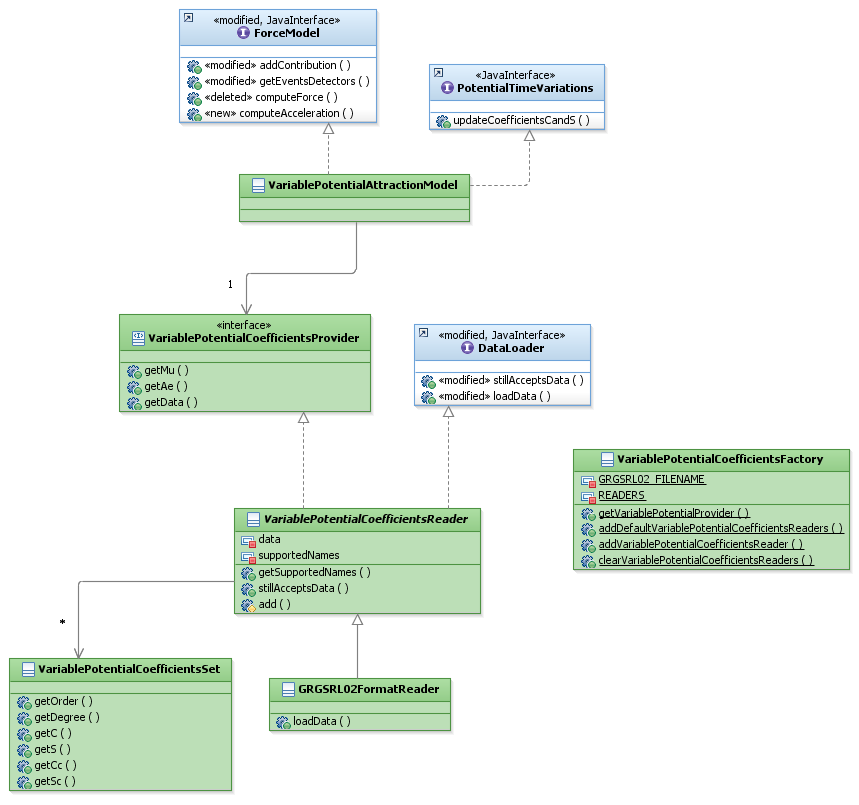
The Orekit org.orekit.forces.gravity.variations package provides tools allowing the user to read external variable gravity potential data files. The corresponding ForceModel is also included in the package. The following file formats are supported by Orekit :
- GRGS RL02
Below is a diagram showing the architecture of the org.orekit.forces.gravity.variations package.
Drag force models
Generalities about Solar Activity and Atmospheres
The atmospheres make use of solar activity in order to compute the density at the given user location excepted US76 model that is only based on altitude parameters. The PATRIUS architecture of atmospheres and solar activity is divided into three layers :
- Atmospheres use solar data in specific ways
Each atmosphere model uses the solar data in a specific way (more simply, US76 doesn't use solar data). These representations are enclosed in the atmosphere model specific interfaces, such as DTM2000InputParamters. Atmosphere models available include US76 (for low altitudes in range 0 to 1000km), DTM2000 and MSISE2000.
- Reading and storing solar data
The way to store the solar data is enclosed in the SolarActivityDataProvider interface. It defines the basic coefficients (Ap, Kp and F10.7 cm) that any solar activity data provider class should be able to return, in order to be compatible with the atmosphere specific implementations (see next point). The solarActivity package contains classes that can read different file formats and can return the solar activity data. So far, one class for each of the ACSOL and NOAA formats has been implemented. Additionally, one class representing constant solar activity (that requires no external file) has been implemented.
- Using the solar data in an adequate fashion
Making effective use of the solar data for specific atmospheres requires an object that provides solar data (implementing the SolarActivityDataProvider) and answers to the interfaces that define the ways in which the atmosphere models use this data (e.g. implementing DTM2000InputParameters). These classes are contained in the org.orekit.forces.atmospheres.solarActivity.specialized package). So far, one class for each of the DTM2000 and MSISE2000 models have been implemented.
Below is a diagram showing the architecture of the org.orekit.forces.atmospheres package. Please note that the org.orekit.forces.atmospheres.solarActivity package follows the same architecture as the org.orekit.forces.gravity.potential package. The user must use the SolarActivityDataFactory class.
For a detailed explanation of the Orekit Data Management System, please refer to the [SUP_DMS_Home Data Management System section] of the Support User Manual.
Atmospheric models
Various models are available in PATRIUS: DTM-2000, MSIS-00, US76, etc. all models inherit the Atmosphere interface providing total density information.
DTM and MSIS models also implement the ExtendedAtmosphere interface which provides more detailed data such as temperature and partial densities of atmosphere constituents.
Some models require solar and geomagnetic information (see below for how to provide solar and geomagnetic data).
MSIS2000 Atmosphere model
The NRLMSISE-00 empirical atmosphere model was developed by Mike Picone, Alan Hedin, and Doug Drob. It describes the neutral temperature and densities in Earth's atmosphere from ground to thermospheric heights. (quoted from [1])
More information can be found at the Naval Research Laboratory website.
In order to use this atmosphere model, the user must proceed by giving the following arguments as inputs to the MSISE2000 class :
- Solar activity data (as a MSISE2000InputParameters)
- the Earth model (as a BodyShape)
- the Sun model (as a CelestialBody)
The following code snippet creates an instance of MSISE2000 :
// Create an instance of the BodyShape "EARTH", with user chosen
// equatorial radius, flattening and body frame
Frame frame = FramesFactory.getITRF();
double f = 0.29825765000000E+03;
double ae = 6378136.46;
BodyShape earth = new OneAxisEllipsoid(ae, 1 / f, frame);
// Get the instance of the CelestialBody "SUN"
CelestialBody sun = CelestialBodyFactory.getSun();
// Create the solar activity data to be used
SolarActivityDataProvider solarActivity = SolarActivityDataFactory.getSolarActivityDataProvider();
final MSISE2000InputParameters msiseData = new ClassicalMSISE2000SolarData(solarActivity);
// Create an instance of the atmosphere model
Atmosphere atmosModel = new MSISE2000(msiseData , earth, sun);
Solar and geomagnetic activity
Solar and geomagnetic activity can be provided in various ways:
- Constant solar activity using:
final SolarActivityDataProvider constantSolarActivity = new ConstantSolarActivity(140, 15);
- Variable solar activity using (for instance):
final SolarActivityDataProvider variableSolarActivity = new NOAAFormatReader(...);
final SolarActivityDataProvider otherVariableSolarActivity = new ACSOLFormatReader(...);
Solar and geomagnetic activity data often having a limited timespan, the class ExtendedSolarActivityWrapper allows data extension with constant values. Solar and geomagnetic data returned before timespan are equals to an average of first available data (the average duration being user-chosen). Solar and geomagnetic data returned after timespan are equals to an average of last available data (the average duration being user-chosen).
These providers are used as inputs of atmospheric models.
Reading Solar Activity Data files
The data is read through the Orekit DataLoader infrastructure; it provides several ways to load solar activity data. Please see the [SUP_DMS_Home Data Management System section] for more information.
The following file formats are supported by PATRIUS:
- ACSOL format
- NOAA format
The user access point is the SolarActivityDataFactory which automatically detects available files and uses the adequate solar file reader. If no file is specified by the user, this factory uses the first available file.
//Directory containing the file ACSOL.act
final File potdir = new File("/my/data/solar");
//The directory is given to the Orekit data loader
DataProvidersManager.getInstance().addProvider(new DirectoryCrawler(potdir));
//The ACSOL file is registered in the SolarActivityDataFactory
//If it is the only solar activity file of the directory, this step is not necessary
SolarActivityDataFactory.addSolarActivityDataReader(new ACSOLFormatReader("ACSOL.act"));
//A provider for the data is created
final SolarActivityDataProvider provider = SolarActivityDataFactory.getSolarActivityDataProvider();
//Get the ap, kp and instant flux at date
final AbsoluteDate userDate = new AbsoluteDate();
final double ap = provider.getAp( userDate );
final double kp = provider.getKp( userDate );
final double f = provider.getInstantFluxValue( userDate );
Tides models
Tides model for force computation =
The PATRIUS org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides package provides tools allowing the user to use Terestrial and Ocean tides. The org.orekit.forces.gravity.tides.coefficients package also allows reading external ocean tides coefficients data files. The following file formats are supported by PATRIUS:
- FES2004 format
Reference point displacement
The PATRIUS org.orekit.utils.ReferencePointsDisplacement class provides a model describing the displacement of reference points due to the effect of the solid Earth tides. The computation is performed by the static method solidEarthTidesCorrections(AbsoluteDate, Vector3D, Vector3D, Vector3D). The implemented model has been validated by comparison with tests available in the IERS website. The example below shows the user how to compute displacements of reference points:
// Test from source ftp://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/chapter7/dehanttideinel/DEHANTTIDEINEL.F
// date : 13/04/2009
final AbsoluteDate date = new AbsoluteDate(2009, 4, 13, 0, 0, 0., TimeScalesFactory.getUTC());
// entries : moon position, sun position, station location
final Vector3D moon = new Vector3D(-179996231.920342,-312468450.131567, -169288918.592160);
final Vector3D sun = new Vector3D(137859926952.015, 54228127881.4350, 23509422341.6960);
final Vector3D point = new Vector3D(4075578.385, 931852.890, 4801570.154);
// compute the displacement
final Vector3D disp = ReferencePointsDisplacement.solidEarthTidesCorrections(date, point, sun, moon);
// comparison with reference results (IERS)
Assert.assertEquals(0.07700420357108125891, disp.getX(), Precision.EPSILON);
Assert.assertEquals(0.06304056321824967613, disp.getY(), Precision.EPSILON);
Assert.assertEquals(0.05516568152597246810, disp.getZ(), Precision.EPSILON);
Geomagnetic models
Design
The Orekit org.orekit.models.earth package provides tools allowing the user to use different geomagnetic models. For the moment, there are only the two following models available :
(% style="margin-left:30px;list-style-type:square;" %)
- IGRF 11 : International Geomagnetic Reference Field eleventh generation
- WMM 2010 : World Magnetic Model published in december 2009
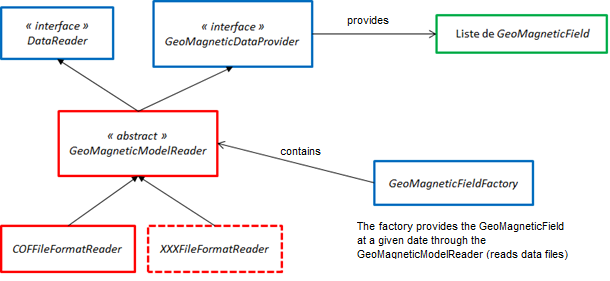
A class diagram is given hereunder to show how geomagnetic is read and used in the library :
The user can create its own GeoMagneticModelReader in order to provide GeoMagneticField from any file format.
IGRF 11 geomagnetic model
The International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF) was introduced by the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) in 1968 in response to the demand for a standard spherical harmonic representation of the Earth's main field. The model is updated at 5-yearly intervals, the latest being the 11th generation, produced and released by IAGA Working Group V-MOD (formerly V-8) December 2009.
More information can be found at the IAGA Division V-Mod.
WMM 2010 geomagnetic model
The World Magnetic Model is a joint product of the United States’ National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) and the United Kingdom’s Defence Geographic Centre (DGC). The WMM was developed jointly by the National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC, Boulder CO, USA) and the British Geological Survey (BGS, Edinburgh, Scotland).
The World Magnetic Model is the standard model used by the U.S. Department of Defense, the U.K. Ministry of Defence, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), for navigation, attitude and heading referencing systems using the geomagnetic field. It is also used widely in civilian navigation and heading systems. The model, associated software, and documentation are distributed by NGDC on behalf of NGA. The model is produced at 5-year intervals, with the current model expiring on December 31, 2014.
The current model, WMM2010 (published 12/2009)
More information can be found at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Details, limitation and precautions
In the geomagnetic field's computation from the different models, to convert geodetic coordinates (defined by the WGS-84 reference ellipsoid) to Earth Centered spherical coordinates, the following constants are used :
- Semi major-axis of WGS-84 ellipsoid : 6378.137 km
- The first eccentricity squared : 0.0066943799901413169961
and to compute the spherical harmonic variables for a given spherical coordinate uses the mean radius of IAU-66 ellipsoid 6371.2 km is used.
The different models are used to compute gemoagnetic field near earth surface. In the model file, the given altitude range of validity is-1 to 600 km even if we can compute field outside of this range.
The method GeoMagneticField.calculateField(final Vector3D point,final Frame frame, final AbsoluteDate date) has been added to Orekit and allows to compute the field from a position vector in a specific frame and at a specific date. This method is based on Orekit tranformModel method which recomputes the field at a date. This method doesn't work if the model doesn't support time transform. In this way, this method added to Orekit throws an Orekit exception about model not supporting time transform.
Here is the list of all possible actual models and the time transform support (please note that only dates prior to 2010 won't support time transformation) :
|Model and associated data file |Model Name|Validity Period|Time transform support |=(% rowspan="23" %)IGRF (% style="font-weight: normal;" %)(GeoMagneticFieldFactory.getIGRF(..) uses IGRF.COF)|IGRF00 | 1900.0 - 1905.0 | false |IGRF05 | 1905.0 - 1910.0 | false |IGRF10 | 1910.0 - 1915.0 | false |IGRF15 | 1915.0 - 1920.0 | false |IGRF20 | 1920.0 - 1925.0 | false |IGRF25 | 1925.0 - 1930.0 | false |IGRF30 | 1930.0 - 1935.0 | false |IGRF35 | 1935.0 - 1940.0 | false |IGRF40 | 1940.0 - 1945.0 | false |DGRF45 | 1945.0 - 1950.0 | false |DGRF50 | 1950.0 - 1955.0 | false |DGRF55 | 1955.0 - 1960.0 | false |DGRF60 | 1960.0 - 1965.0 | false |DGRF65 | 1965.0 - 1970.0 | false |DGRF70 | 1970.0 - 1975.0 | false |DGRF75 | 1975.0 - 1980.0 | false |DGRF80 | 1980.0 - 1985.0 | false |DGRF85 | 1985.0 - 1990.0 | false |DGRF90 | 1990.0 - 1995.0 | false |DGRF95 | 1995.0 - 2000.0 | false |DGRF2000 | 2000.0 - 2005.0 | false |DGRF2005 | 2005.0 - 2010.0 | false |IGRF2010 | 2010.0 - 2015.0 | true |=(% rowspan="1" %)WMM (% style="font-weight: normal;" %)(GeoMagneticFieldFactory.getWMM(..) uses WMM.COF)(%%) | WMM2010 | 2010.0 - 2015.0 | true
Precautions : The method GeoMagneticField.calculateField (final double latitude, final double longitude, final double height) doesn't use SI units. Latitude and longitude are given in degrees, and height is given in kilometers.
Code Example
The following code snippet computes geomagnetic field elements for four (date, position) of a fake trajectory :
public void codeExemple() throws OrekitException{
Utils.setDataRoot("earth");
FramesFactory.setConfiguration(Utils.getIERS2003ConfigurationWOEOP(true));
//Fake trajectory : list of date and list of position
List<AbsoluteDate> dateList = new ArrayList<AbsoluteDate>();
AbsoluteDate initDate = new AbsoluteDate(2010, 1, 1, 12, 0, 0.0, TimeScalesFactory.getTT());
dateList.add(initDate);
dateList.add(new AbsoluteDate(initDate, 600));
dateList.add(new AbsoluteDate(initDate, 1200));
dateList.add(new AbsoluteDate(initDate, 1800));
List<Vector3D> positionList = new ArrayList<Vector3D>();
positionList.add(new Vector3D(6.46885878304673824e+06,-1.88050918456274318e+06, -1.32931592294715829e+04));
positionList.add(new Vector3D(6.58239141552595049e+06,-1.43349476017528563e+06, -1.39460373997706010e+04));
positionList.add(new Vector3D(6.66499609614125639e+06,-9.79745192516532145e+05, -1.45334684008149434e+04));
positionList.add(new Vector3D(6.71628402448997274e+06,-5.21392324304617418e+05, -1.50526405214286660e+04));
// Get the model to the initial date
final GeoMagneticField model = GeoMagneticFieldFactory.getIGRF(dateList.get(0));
// For each date and position, compute the GeoMagneticElement and add it to a list
List<GeoMagneticElements> geoMagList = new ArrayList<GeoMagneticElements>();
int i = 0;
for (AbsoluteDate date : dateList){
geoMagList.add(model.calculateField(positionList.get(i), FramesFactory.getEME2000(), date));
}
// Print each field vector B
for (GeoMagneticElements geoMagElement : geoMagList){
System.out.println(geoMagElement.toString());
}
}
This code produces the following standard output :
MagneticField[B={29817,109;-2303,065; -9138,097},H=29905,92,F=31270,895,I=-16,991,D=-4,417]
MagneticField[B={29442,018;-2166,283; -8949,299},H=29521,606,F=30848,261,I=-16,864,D=-4,208]
MagneticField[B={29067,408;-1996,393; -8794,324},H=29135,885,F=30434,19,I=-16,796,D=-3,929]
MagneticField[B={28695,713;-1796,821; -8680,411},H=28751,913,F=30033,681,I=-16,799,D=-3,583]
Getting Started
Modèle:SpecialInclusion prefix=$theme sub section="GettingStarted"/
Contents
Interfaces
|=(% colspan="3" %)Interface|=(% colspan="6" %)Summary|=(% colspan="1" %)Javadoc |(% colspan="3" %)Atmosphere|(% colspan="6" %)Interface for atmospheric models.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ExtendedAtmosphere|(% colspan="6" %)Interface for atmospheric models with detailed data.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)SolarActivityDataProvider|(% colspan="6" %)Interface for solar activity data providers, to be used for atmosphere models|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)DTM2000InputParameters|(% colspan="6" %)Container for solar activity data, compatible with DTM2000 Atmosphere model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)MSISE2000InputParameters|(% colspan="6" %)Container for solar activity data, compatible with MSISE2000 Atmosphere model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)OceanTidesCoefficientsProvider|(% colspan="6" %)This interface is used to provide ocean tides coefficients.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)PotentialCoefficientsProvider|(% colspan="6" %)This interface is used to provide gravity field coefficients.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)VariablePotentialCoefficientsProvider|(% colspan="6" %)This interface is used to provide variable gravity field coefficients.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)**RadiationSensitive|(% colspan="6" %)This interface is used to provide an direct solar radiative pressure model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)**RediffusedRadiationSensitive|(% colspan="6" %)This interface is used to provide an rediffused radiative pressure model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GeoMagneticDataProvider|(% colspan="6" %)This interface is a generic geomagnetic data provider.|(% colspan="1" %)...
Classes
Earth potential
|=(% colspan="3" %)Class|=(% colspan="6" %)Summary|=(% colspan="1" %)Javadoc |(% colspan="3" %)EGMFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)This reader is adapted to the EGM Format.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GravityFieldFactory|(% colspan="6" %)Factory used to read gravity field files in several supported formats. Main user access point : the simple way of reading a potential file is by using this factory.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)VariableGravityFieldFactory|(% colspan="6" %)Factory used to read variable gravity field files in several supported formats. Main user access point : the simple way of reading a variable potential file is by using this factory.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GRGSFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)Reader for the GRGS gravity field format.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GRGSRL02FormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)Reader for the GRGS RL02 variable gravity field format.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ICGEMFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)Reader for the ICGEM gravity field format.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)PotentialCoefficientsReader|(% colspan="6" %)This abstract class represents a Gravitational Potential Coefficients file reader.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)SHMFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)Reader for the SHM gravity field format.|(% colspan="1" %)...
Atmosphere Models
|=(% colspan="3" %)Class|=(% colspan="6" %)Summary|=(% colspan="1" %)Javadoc |(% colspan="3" %)DTM2000|(% colspan="6" %)This class implements the DTM2000 atmospheric model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)JB2006|(% colspan="6" %)This class implements the JB2006 atmospheric model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)MSISE2000|(% colspan="6" %)This class implements the MSIS00 atmospheric model.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)US76|(% colspan="6" %)This class implements the US76 atmospheric model.|(% colspan="1" %)...
Solar Activity |=(% colspan="3" %)Class|=(% colspan="6" %)Summary|=(% colspan="1" %)Javadoc |(% colspan="3" %)DTM2000SolarData|(% colspan="6" %)This class represents a solar data container adapted for the DTM2000 atmosphere model|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ClassicalMSISE2000SolarData|(% colspan="6" %)This class represents a solar data container adapted for the MSISE2000 atmosphere model. The average ap values are computed arithmetically.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ContinuousMSISE2000SolarData|(% colspan="6" %)This class represents a solar data container adapted for the MSISE2000 atmosphere model. The mean ap values are computed by trapezoidal integration.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ACSOLFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)This class reads ACSOL format solar activity data|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ConstantSolarActivity|(% colspan="6" %)This class represents constant solar activity|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)NOAAFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)This class reads NOAA format solar activity data|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)SolarActivityDataFactory|(% colspan="6" %)Factory used to read solar activity files and return SolarActivityDataProvider|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)SolarActivityToolbox|(% colspan="6" %)Solar activity toolbox. Has methods to compute mean flux values, to convert from ap to kp.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)MarshallSolarActivityFutureEstimation|(% colspan="6" %)This class reads and provides solar activity data needed by atmospheric models: F107 solar flux and Kp indexes.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)ExtendedSolarActivityWrapper|(% colspan="6" %)This class extends a solar activity provider out of its timespan with constant values.|(% colspan="1" %)...
Ocean Tides Coefficients
|=(% colspan="3" %)Class|=(% colspan="6" %)Summary|=(% colspan="1" %)Javadoc |(% colspan="3" %)FES2004FormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)Reader for FES2004 format coefficients files.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)OceanTidesCoefficientsFactory|(% colspan="6" %)Factory used to read ocean tides coefficients files in different formats and return an OceanTidesCoefficientsProvider.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)OceanTidesCoefficientsReader|(% colspan="6" %)This abstract class represents a Ocean Tides Coefficients file reader.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)OceanTidesCoefficientsSet|(% colspan="6" %)Represents a line from the ocean tides data file.|(% colspan="1" %)...
Geomagnetic Field
|=(% colspan="3" %)Class|=(% colspan="6" %)Summary|=(% colspan="1" %)Javadoc |(% colspan="3" %)GeoMagneticElements|(% colspan="6" %)This class contains all the elements about a magnetic field : the magnetic field vector and associated caracteristics Inclination, Declination, Total Intensity, Horizontal Intensity.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GeoMagneticField|(% colspan="6" %)These objects are produced by the factory and are based on a model for a decimal year date and allows to compute GeomagneticElements |(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GeoMagneticFieldFactory|(% colspan="6" %)Factory to produce GeoMagneticField.|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)GeoMagneticModelReader|(% colspan="6" %)To load the model from an input file|(% colspan="1" %)... |(% colspan="3" %)COFFileFormatReader|(% colspan="6" %)Class loading the geomagnetic data from COF files.|(% colspan="1" %)...