User Manual 4.0 Parallelepipeds : Différence entre versions
De Wiki
(Page créée avec « ====Definition==== The parallelepipeds are rectangles defined in a 3D space by their centre and a local orthogonal frame (U, V, W). * The normalized U vector defines the... ») |
(Aucune différence)
|
Version actuelle en date du 4 avril 2018 à 08:12
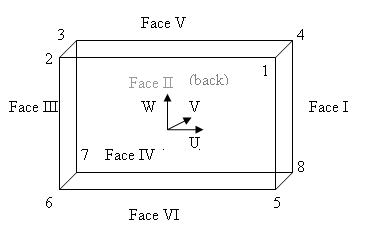
Definition
The parallelepipeds are rectangles defined in a 3D space by their centre and a local orthogonal frame (U, V, W).
- The normalized U vector defines the "length" direction
- The normalized V vector defines the "width" direction
- The normalized W vector defines the "height" direction
The four corners and faces can be retrieved in the following orders :
Implementation
The Parallelepiped object implements the SolidShape interface. Please refer to the Parallelepiped javadoc for a complete list of public methods.
Instantiation
The parallelepiped object is built from a centre (Vector3D), two vectors (Vector3D) to describe its orientation, and three dimensions :
Vector3D center = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); Vector3D uVector = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 0.0); Vector3D inputvVector = new Vector3D(-5.0, 1.0, 0.0); Parallelepipedparallelepiped= new Parallelepiped(center, uVector, inputvVector, 4.0, 6.0, 2.0);
The local frame of the plate is build from the two orientation vector :
- U is the first once normalized (uVector)
- V is the vector computed to be orthogonal to U in the plane define by the two given vectors, in the direction of inputvVector.
- W is computed by cross product of U and V
Usage
Please refer to the [MAT_GEO_Home#HInteractions Interactions with other geometrical objects section] for methods inherited from the Shape interface.