« User Manual 3.4.1 Facets » : différence entre les versions
Aucun résumé des modifications |
|||
| Ligne 10 : | Ligne 10 : | ||
====Implementation==== | ====Implementation==== | ||
This class implements the CrossSectionProvider interface (org.apache.commons.math.geometry.euclidean.threed).<br> | This class implements the CrossSectionProvider interface (org.apache.commons.math.geometry.euclidean.threed).<br> | ||
Please refer to the [{{ | Please refer to the [{{JavaDoc3.4.1}}/fr/cnes/sirius/patrius/assembly/properties/features/Facet.html Javadoc] for a complete list of public methods. | ||
====Instantiation==== | ====Instantiation==== | ||
Dernière version du 4 avril 2018 à 13:57
Definition
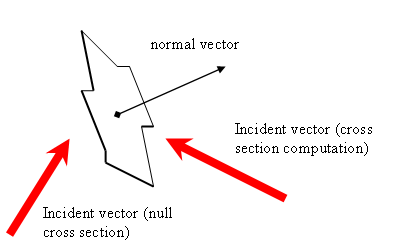
A facet is a surface defined by its area and a normal vector, no supposition made of its exact shape.
From those information, it can compute its cross section seen from any incidental vector.
A facet is visibile only from one half-space : the cross section computed is not null only if the dot product with the incidental vector is negative.
It shall be used to describe a spacecraft geometry in cross section computations for force models.
Implementation
This class implements the CrossSectionProvider interface (org.apache.commons.math.geometry.euclidean.threed).
Please refer to the Javadoc for a complete list of public methods.
Instantiation
The Facet class is built from its area and normal vector :
Vector3D normalvector = new Vector3D(1.0, 5.6,-3.2);
CrossSectionProvider facet = new Facet(normalvector , 5.0);
Usage
The Facet class proposes basic methods to get its area and normal vector.
It also provides the method getCrossSection (CrossSectionProvider interface), that shall be used this way :
Vector3D incidentialBeam = new Vector3D(7.0,-2.0, 8.0);
double crossSection = facet.getCrossSection(incidentialBeam);
The result is not null only if "incidentialBeam " dot product with "normalvector " is negative.