User Manual 4.1 Attitude ephemeris : Différence entre versions
De Wiki
(Page créée avec « __NOTOC__ == Introduction == === Scope === The purpose is to extend the attitude package with classes and methods to compute and process attitude ephemeris. === Javadoc =... ») |
(Aucune différence)
|
Version actuelle en date du 28 juin 2018 à 12:32
Introduction
Scope
The purpose is to extend the attitude package with classes and methods to compute and process attitude ephemeris.
Javadoc
The ephemeris objects are available in the package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.attitudes.
| Library | Javadoc |
|---|---|
| Patrius | Package fr.cnes.sirius.patrius.attitudes |
Links
Orekit attitudes : Orekit Attitudes architecture description
Useful Documents
None as of now.
Package Overview
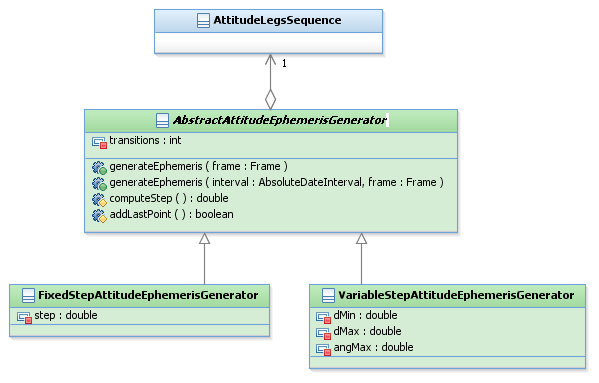
The attitude ephemeris conception is described hereafter :
Legend :
- green : new objects
- grey : modified existing objects
- blue : existing objects
Features Description
Generation of attitude ephemeris
Attitude ephemeris are generated from a sequence of attitude laws using a fixed time step; one or more options can be added when computing ephemeris:
- the time interval of generation can be smaller than the attitude laws sequence time interval (but it must be contained in it);
- attitude can be computed when there is a transition between attitude laws in the sequence: the user can choose to compute one value (the attitude of the law starting at the transition point), or two values (the attitude of the law starting and that of the law ending at the transition point);
- the time step can be variable: in this case, the user must choose a minimum and maximum time step, and a threshold value for the angular distance. The time step is then computed for each ephemeris; the angular distance between two consecutive ephemeris is calculated: when is bigger than the threshold value, the time step is reduced using an iterative algorithm.
Getting Started
Here are given code sample for fixed and variable step ephemeris generation.
Fixed step ephemeris generation
final AbsoluteDate date0 = AbsoluteDate.J2000_EPOCH; final AbsoluteDate dateF = date0.shiftedBy(86400); final AbsoluteDateInterval interval = new AbsoluteDateInterval(IntervalEndpointType.OPEN, date0, dateF, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN); AttitudeLegsSequence sequence = new AttitudeLegsSequence(orbit); double fixedStep = 10; FixedStepAttitudeEphemerisGenerator generator = new FixedStepAttitudeEphemerisGenerator(sequence, fixedStep); final Set<Attitude> ephemeris = generator.generateEphemeris(interval, FramesFactory.getGCRF());
Variable step ephemeris generation
final AbsoluteDate date0 = AbsoluteDate.J2000_EPOCH; final AbsoluteDate dateF = date0.shiftedBy(86400); final AbsoluteDateInterval interval = new AbsoluteDateInterval(IntervalEndpointType.OPEN, date0, dateF, IntervalEndpointType.OPEN); AttitudeLegsSequence sequence = new AttitudeLegsSequence(orbit); final double stepMin = 1; final double stepMax = 10; final double angMax = 0.15; VariableStepAttitudeEphemerisGenerator generator = new VariableStepAttitudeEphemerisGenerator(sequence, stepMin, stepMax, angMax, AbstractAttitudeEphemerisGenerator.START_TRANSITIONS); final Set<Attitude> ephemeris = generator.generateEphemeris(interval, frame);
Contents
Interfaces
None as of now.
Classes
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| AbstractAttitudeEphemerisGenerator | Abstract class containing the methods to generate attitude ephemeris from an attitude laws sequence. | ... |
| FixedStepAttitudeEphemerisGenerator | Class computing attitude ephemeris from an attitude laws sequence, using a fixed time step. | ... |
| VariableStepAttitudeEphemerisGenerator | Class computing attitude ephemeris from an attitude laws sequence, using a variable time step. | ... |