User Manual 3.3 Lines
Definition
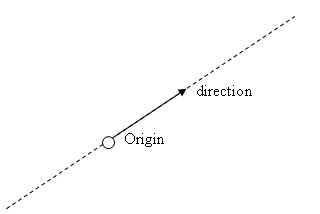
The lines are defined by an origin point and a direction vector (both Vector3D).
Implementation
Please refer to the Javadoc for a complete list of public methods.
Instantiation
A Line(geometry.euclidian.threed) can be created in twi different ways :
- Using the constructor, by giving it two different points of the line.
Vector3D p1 = new Vector3D(8, -12, 2);
Vector3D p2 = new Vector3D(-3, 4, 1);
Line l2 = new Line(p1, p2, true);
- Using the static method createLine(Vector3D, Vector3D) : the first Vector3D is a point of the line, the second one is the direction.
Vector3D origin = new Vector3D(-6, 4, 2);
Vector3D direction = new Vector3D(2, 0, -9);
Line l1 = Line.createLine(origin, direction );
The origin of the line is always computed to be the closest one of the line to the (0, 0, 0) point.
Usage
The Line class proposes methods to :
- Test if the line identical to another one (they are similar if the contain the same points) :
boolean similarLines = line1.isSimilarTo(line2);
- the coordinates of the projection of any point of space in the local frame (origin, direction)
Vector3D point = new Vector3D(2, 3, 5);
Vector1D pointOnLine = line.toSubSpace(point);
- the coordinates in the global frame of a point expressed in the local frame
Vector3D point = p1.toSpace(pointOnLine );
- Test if a point belongs to it
Vector3D point = new Vector3D(2, 3, 5);
boolean containsPoint = line1.contains(point);
Please refer to the Interactions with other geometrical objects section for other methods : Line does not implement the Shape interface (it is not a "shape"), but contains methods for interactions with other lines and points (clostestPointTo, distance...).