User Manual 3.3 Geometry
Introduction
Scope
The geometry objects implemented in the PATRIUS library are both infinite and finite shapes.
The finite shapes shall be used for example to represent parts of a spacecraft or celestial bodies. The infinite ones can represent more mathematical surfaces such as instruments' characteristics.
All the objects provide methods to compute interactions with lines (intersections, distances, etc...), points and other objects.
Javadoc
The geometry objects are available in the package org.commons.math3.geometry.euclidean.threed in the Commons Math Library (and Commons Math add-ons).
| Library | Javadoc |
|---|---|
| Commons Math | Package org.commons.math3.geometry.euclidean.threed |
| Commons Math addons | Package org.commons.math3.geometry.euclidean.threed |
Links
Commons Math contains several other packages related to geometry (1D, 2D, 3D) and provides objects for Binary Space Partitioning (BSP) Tree. See javadoc for more information. Some other "basic" objects are contained in the Commons Math threed package and documented in other parts of this manual (eg : Rotations, Matrix3D).
Useful Documents
Useful reference documents for this theme can be found here :
- Nürnberg, R.; Distance from a Point to an Ellipse, Imperial College London, 2006, http://www2.imperial.ac.uk/~~rn/distance2ellipse.pdf.
Package Overview
The aim of the following diagram is to present the architecture implemented for the Geometry package. This does not mean that all the classes and/or interfaces are in the Geometry package and it doesnt mean that all the classes and interfaces of the package are presented.
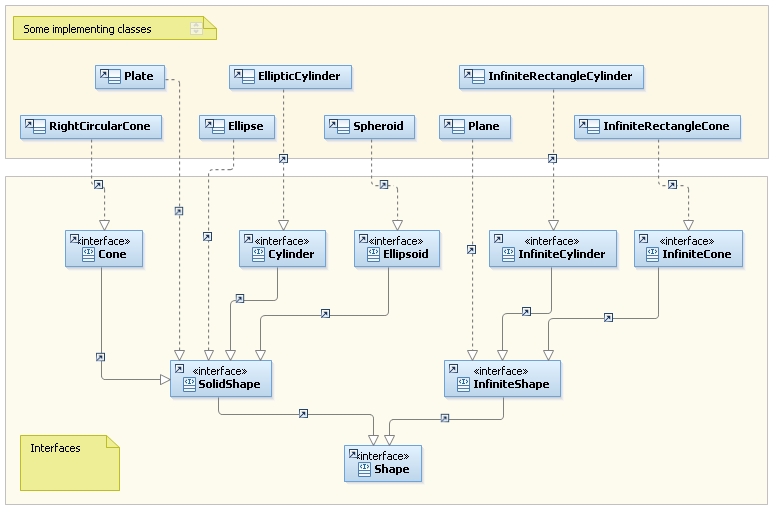
Features Description
2D Objects
The two dimensional objects (in three dimensional space) implemented in the PATRIUS library are given hereunder :
- Lines
- Planes
- Plates
- Disks
- Ellipses
Please refer to the Classes section for more information.
3D Objects
The three dimensional objects (in three dimensional space) implemented in the PATRIUS library are given hereunder :
- Infinite and Finite Cylinders (right circular, elliptic and rectangular)
- Infinite and Finite Cones (right circular, oblique circular and rectangular)
- Spheres, Spheroids and Spherical Caps
- Parallelepipeds
Please refer to the Classes section for more information.
Interactions between objects
Interfaces have been implemented for geometrical objects in order to set a standard as to what method each and any geometrical object should implement.
As of now, (some of the) geometrical objects must provide methods to :
- Check if a line intersects with said objects,
- Compute and return the intersection points,
- Compute and return the closest point on the object surface to a given user point,
- Compute and return the distance between these two points,
- Compute and return the closest point on the object surface to a given user line and return the closest points on the line and on the object,
- Compute and return the distance between an object and a given user line.
Plese refer to the Interactions section for more details.
Getting Started
Modèle:SpecialInclusion prefix=$theme sub section="GettingStarted"/
Contents
Interfaces
| Interface | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| Cone | This interface extends the SolidShape interface for the particular case of cones. | ... |
| CrossSectionProvider | Interface for all geometric objects that can provide their cross section from a direction defined by a Vector3D. | ... |
| Cylinder | This interface extends the SolidShape interface for the particular case of cylinders. | ... |
| IEllipsoid | This interface extends the InfiniteShape interface for the particular cases of ellipsoid objects. | ... |
| InfiniteCone | This interface extends the InfiniteShape interface for the particular cases of infinite cones. | ... |
| InfiniteCylinder | This interface extends the InfiniteShape interface for the particular cases of infinite cylinders. | ... |
| InfiniteShape | This interface extends the Shape interface for the particular cases of infinite shapes. | ... |
| Shape | This interface is the main interface for all shapes, including infinite and solid shapes. It defines the general methods required by each geometrical object implementing any of the above interfaces : All of them must be able to compute their intersection and distance to a line. See [MAT_GEO_Home#HInteractionsbetweenobjects Interactions]. | ... |
| SolidShape | This interface extends the Shape interface for the particular cases of solids. | ... |
Classes
Basic Shapes
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| Disk | The class represent disks in a three dimensional space. | ... |
| Ellipse | The class represent ellipses in a three dimensional space. | ... |
| Plane | The class represent lines in a three dimensional space. | ... |
| Plane | The class represent planes in a three dimensional space. | ... |
| Plate | This is a describing class for a 3D rectangle plate shape, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| Parallelepiped | This is a describing class for a rectangle parallelepiped shape, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
Cylinders
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| InfiniteEllipticCylinder | This class is the Infinite Elliptic Cylinder class. | ... |
| InfiniteRightCircularCylinder | This is a describing class for a 3D infinite right circular cylinder, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| InfiniteRectangleCylinder | This is a describing class for a 3D infinite rectangle cylinder, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| InfiniteRightCircularCone | This is a describing class for a 3D oblique circular cylinder ended by two planes normal to its axis, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| InfiniteRightCircularCone | This is a describing class for a 3D right circular cylinder ended by two planes normal to its axis, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
NB : For the rectangular cylinder, please refer to the parallelepiped class mentioned above.
Cones
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| InfiniteRightCircularCone | This is a describing class for a 3D infinite cone, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| InfiniteRectangleCone | This class is the Infinite Elliptic Cone class. | ... |
| InfiniteRectangleCone | This is a describing class for a 3D infinite cone, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| Ellipsoid] | This is a describing class for a 3D right circular cone ended by a plane normal to its axis, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| Ellipsoid | This is a describing class for a 3D elliptic cone ended by a plane normal to its axis, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| Ellipsoid | This is a describing class for a 3D rectangle cone ended by a plane normal to its axis (pyramid), with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
Ellipsoids
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| Ellipsoid | This is a describing class for an ellipsoid, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| Sphere | This is a describing class for a 3D spherical shape, with some algorithm to compute intersections and distances to some other objects. | ... |
| Spheroid | This is the Spheroid (also called Revolved Ellipsoid) class. | ... |
Other objects
| Class | Summary | Javadoc |
|---|---|---|
| Facet | Implements a representation of a facet. | ... |
| Spherical Caps | Implements a representation of a spherical cap solid. | ... |
Interactions
Given an object implementing the Shape interface, the following methods are available :
intersects(Line) : boolean
Test the intersection of the object with a user given line.
Code snippet :
Line line = new Line(lineOrigin, lineDirection);
boolean result = myObject.intersects(line);
getIntersectionPoints(Line) : Vector3D[]
Compute the intersection point of the object with a user given line.
Code snippet :
Line line = new Line(lineOrigin, lineDirection);
Vector3D[] intersectionPoints = myObject.getIntersectionPoints(line);
closestPointTo(Vector3D) : Vector3D
Compute the point on the surface of the object that is the closest to a user given point.
Code snippet :
Vector3D point = new Vector3D(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
Vector3D result = myObject.closestPointTo(point);
distanceTo(Vector3D) : double
Compute the shortest distance from the surface of the object and user given point.
Code snippet :
Line line = new Line(lineOrigin, lineDirection);
double distance = myObject.distanceTo(line);
closestPointTo(Line) : Vector3D[]
Compute the points realizing the shortest distance to a line (the first one is from the line, the second one from the object ). If the line intersects the object , the two points are identical, and equal to the first one returned by the "getIntersectionPoints" method. If the line is parallel to the object 's side, the closest point to the origin is used.
Code snippet :
Line line = new Line(lineOrigin, lineDirection);
Vector3D[] points = myObject.closestPointTo(line);
distanceTo(Line) : double
Compute the shortest distance from a line to the surface of the object.
Code snippet :
Line line = new Line(lineOrigin, lineDirection);
double distance = myObject.distanceTo(line);
Tutorials
Tutorial 1
Modèle:SpecialInclusion prefix=$theme sub section="Tuto1"/
Tutorial 2
Modèle:SpecialInclusion prefix=$theme sub section="Tuto2"/
 Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks
None as of now.