User Manual 3.3 Infinite Rectangle Cylinder
Definition
The infinite rectangle cylinders are defined in a 3D space by their axis (a line or two equivalent vectors origin and direction), the direction of their local frame U vector and their two dimensions (length on the U axis and width on V) :
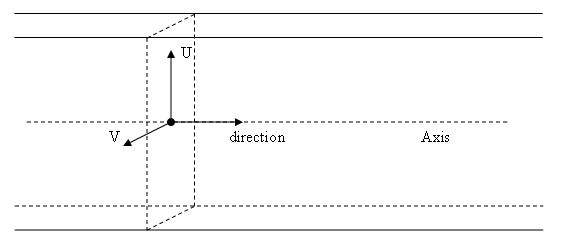
Implementation
The Infinite Rectangle Cylinder object in the SIRIUS library implements the infinite cylinder interface and has the following constructor and public methods :
- InfiniteEllipticCylinder(Vector3D, Vector3D, double, double)
- intersects(Line) : boolean
- getIntersectionPoints(Line) : Vector3D[]
- closestPointTo(Line) : Vector3D[]
- distanceTo(Line) : double
Please refer to the Javadoc for a complete list of public methods.
Instantiation
The object is built from three vectors (Vector3D) and two doubles :
Vector3D origin = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
Vector3D direction = new Vector3D(2.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Vector3D inputUvector = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
double length = 2.0;
double width = 4.0;
InfiniteRectangleCylindercylinder = new InfiniteRectangleCylinder(origin, direction, inputUvector, length, width);
Or directly from a Line, a non-colinear vector and two doubles :
Line axis = new Line(origin, direction);
Vector3D inputUvector = new Vector3D(1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
double length = 2.0;
double width = 4.0;
InfiniteRectangleCylindercylinder = new InfiniteRectangleCylinder(axis, inputUvector, length, width);
The local frame is built such as :
- The axis is the W vector
- U is orthogonal to W and its direction is defined by the 'input U vector"
- V completes the frame
Usage
Please refer to the [MAT_GEO_Home#HInteractions Interactions with other geometrical objects section] for methods inherited from the Shape interface.